Test Suite: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(ascii art tweaks) |
(ascii tweaks) |
||
| Line 99: | Line 99: | ||
=== State of the ASCII Art === | === State of the ASCII Art === | ||
LEFT | LEFT RIGHT | ||
-----------------------------+------------------------- 192.0.3.0/24 | -----------------------------+-------------------------- 192.0.3.0/24 | ||
| | | | ||
192.0.3.254(eth0) | 192.0.3.254(eth0) | ||
| Line 121: | Line 121: | ||
| | | | ||
------+------------------------------------------------ 192.0.1.0/255 | ------+------------------------------------------------ 192.0.1.0/255 | ||
------------------------------------------------------- 192.1.4.0/255 | ------------------------------------------------------- 192.1.4.0/255 | ||
Revision as of 20:32, 25 April 2022
Running tests
The libreswan tests, in testing/pluto, can be run using several different mechanisms:
| Framework | Speed | Host | Guest | Modifies / | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Namespaces | fast | linux | linux | yes | results are host dependent (for instance the host's kernel version) requires all dependencies, including libreswan, to be installed on / no systemd tests |
| KVM | slower | generic? | Fedora, OpenBSD | no | in theory it can be run on any system supporting libvirt/KVM (but only Linux has ever been used) |
| Docker | linux | Linux centric using host kernel. Ideal for build tests. Can build using various Linux Distributions : CentOS 6, 7, 8, Fedora 28 - rawhide, Debian, Ubuntu. Also for run tests using systemd. |
How tests work
All the test cases involving VMs are located in the libreswan directory under testing/pluto/. The most basic test case is called basic-pluto-01. Each test case consists of a few files:
- description.txt to explain what this test case actually tests
- ipsec.conf files - for host west is called west.conf. This can also include configuration files for strongswan or racoon2 for interop testig
- ipsec.secret files - if non-default configurations are used. also uses the host syntax, eg west.secrets, east.secrets.
- An init.sh file for each VM that needs to start (eg westinit.sh, eastinit.sh, etc)
- One run.sh file for the host that is the initiator (eg westrun.sh)
- Known good (sanitized) output for each VM (eg west.console.txt, east.console.txt)
- testparams.sh if there are any non-default test parameters
Once the test run has completed, you will see an OUTPUT/ directory in the test case directory:
$ ls OUTPUT/ east.console.diff east.console.verbose.txt RESULT west.console.txt west.pluto.log east.console.txt east.pluto.log swan12.pcap west.console.diff west.console.verbose.txt
- RESULT is a text file (whose format is sure to change in the next few months) stating whether the test succeeded or failed.
- The diff files show the differences between this testrun and the last known good output.
- Each VM's serial (sanitized) console log (eg west.console.txt)
- Each VM's unsanitized verbose console output (eg west.console.verbose.txt)
- A network capture from the bridge device (eg swan12.pcap)
- Each VM's pluto log, created with plutodebug=all (eg west.pluto.log)
- Any core dumps generated if a pluto daemon crashed
- testing/baseconfigs/
- configuration files installed on guest machines
- testing/guestbin/
- shell scripts used by tests, and run on the guest
- testing/linux-system-roles.vpn/
- ???
- testing/packaging/
- ???
- testing/pluto/TESTLIST
- list of tests, and their expected outcome
- testing/pluto/*/
- individual test directories
- testing/programs/
- executables used by tests, and run on the guest
- testing/sanitizers/
- filters for cleaning up the test output
- testing/utils/
- test drivers and other host tools
- testing/x509/
- certificates, scripts are run on a guest
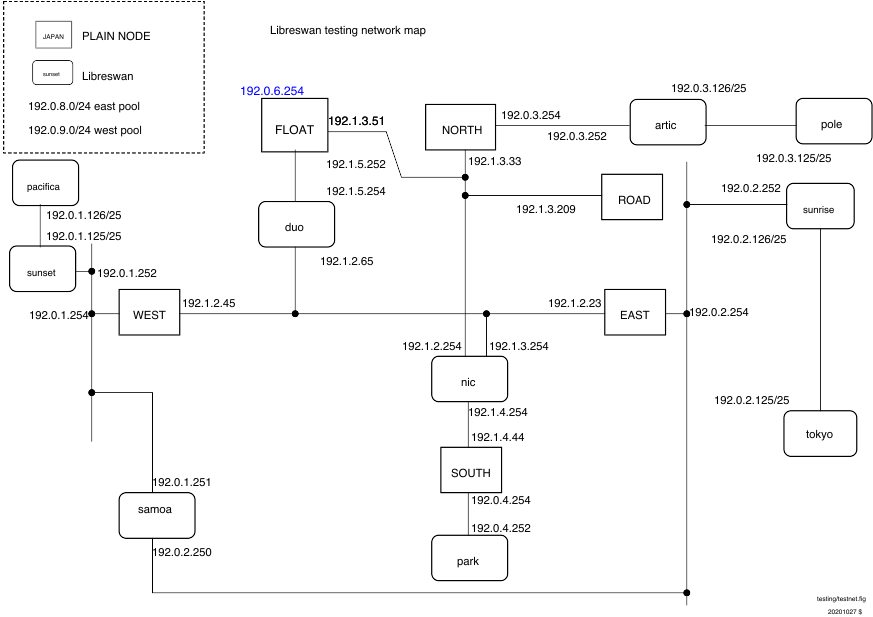
Network Diagrams
Fine Print
- (mostly) interface-0 (eth0, vio0, vioif0) is connected to SWANDEFAULT which has a NAT gateway to the internet
- the exceptions are the Fedora test domains: EAST, WEST, ROAD, NORTH; should they?
- the BSD domains always up inteface-0 so that /pool, /source, and /testing can be NFS mounted
- NIC needs to run DHCP on eth0 manually; how?
- transmogrify does not try to change interface-0's connection to SWANDEFAULT (it breaks network connections, such as NFS, established)
- the interface names are for Fedora
- OpenBSD uses vioN (different order)
- NetBSD uses vioifN (in a different order)
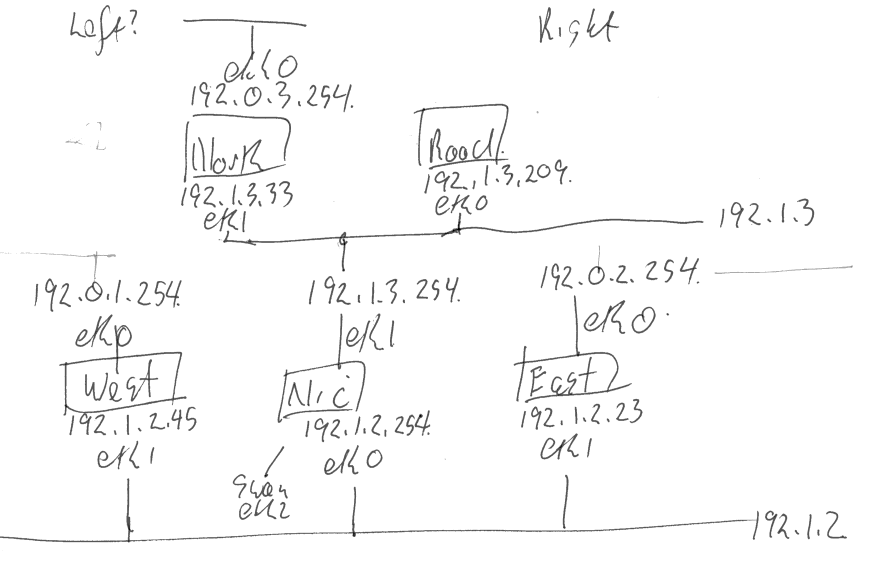
State of the ASCII Art
LEFT RIGHT
-----------------------------+-------------------------- 192.0.3.0/24
|
192.0.3.254(eth0)
ROAD NORTH
192.1.3.209(eth0) 192.1.3.33(eth1)
| |
------+----------------------+-------+----------------- 192.1.3.0/254
|
192.1.3.254(eth2)
NIC--------------[swandefault(0)]
192.1.2.254(eth1)
|
------+------------------------------+--------+-------- 192.1.2.0/24
| |
192.1.2.45(eth1) 192.1.2.23(eth1)
WEST----- [swandefault(0)] EAST----[swandefault(0)]
192.0.1.254(eth0) 192.0.2.254(eth0)
| |
| -----+-------- 192.0.2.0/255
|
------+------------------------------------------------ 192.0.1.0/255
------------------------------------------------------- 192.1.4.0/255